Understanding student loans, pay-back options
Student loan debt is something that student have been scared about thinking about, especially talking to counselors and looking at random sites for money for school, but things seem to be changing in the current climate. The idea for removing the cost for college isn’t a new one, with many countries opting to pay for most or all of your college tuition in exchange for more taxes or promise to invest, but in the US we have opted for a more off handed approach with heavy financial aid as a substitute. This substitute hasn’t always worked or been readily available though, so many have called for a better way to either pay off college debt or canceling off debt to help with the current economic situation the US is going through at the moment.
So this calls for understanding how student debt works and what the current Biden administration is trying to do with student debt.
Student debt, as scary as that sounds, isn’t the end of the world. Student debt is only the money you owe for going to a specific university/school system that the government then loans you so you can attend. This is separate from grants and scholarships, which are more like gifts. Instead loans in this manner have to actually be paid back to the government over a set amount of time. These types of loans from the government can come in multiple different forms, from subsidized loans to consolidation loans, that affect how students will be paying back their money to the federal government. There are two types of direct loans where if subsidized will only accrue interest when students graduate from your school, while unsubsidized will be accruing interest even while students attend school. There are then two other types of loans that students can get, with a PLUS loan filling the gap for any amount that hasn’t been paid off for anything else. The last type is a consolidation loan, which allows students the ability to combine all their federal student loans into a single loan. Most of these offerings come from FAFSA, which offers these types of loans to students to complete their schooling process. So these loans would all be taken into account when students don’t have any grants or scholarships then students would be looking for the subsidized or unsubsidized loans to get the most out and pay off easily, subsidized being a better option, but is only available if they qualify for certain standards and their dependency on your parents. A Plus loan would be good filler for any money that students didn’t accrue from grants/scholarships, but its debt accruement can still hit the wallet heavily if they aren’t careful with your money. Finally a consolidation loan is good to help with paying off final payments and getting papers in order, which can be beneficial for filing taxes/making it easier to pay it off in the long run.
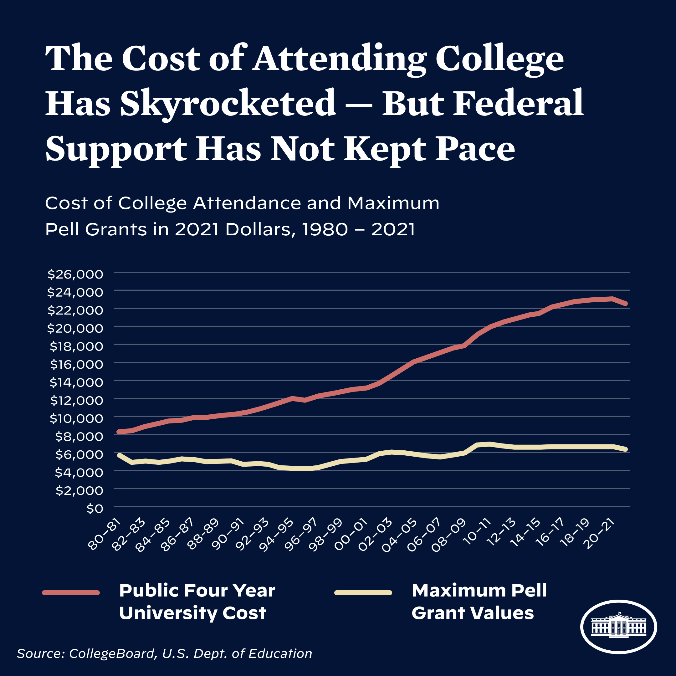
The list of debt to the federal government, as fun as that sounds, leaves a lot to question how to pay back loans with a fixed interest rate ranging from 4.99% to 7.54%.
According to the studentaid.gov website, the current interest rate of all student loans is 0 percent through Dec 31, 2022. While that is right around the corner, the Biden administration is currently working on and passing legislation that is meant to extend this even further and forgive some of the debt accumulated over the past few years to help with economic relief from the covid-19 pandemic. The first part of the plan is most apparent to every college student no matter their loans, the final push back to pay loans, with loans starting their accruement back in January of 2023. The second part of the plan is a transitory cancellation of debts for loans across the board, with up to twenty thousand dollars of cancellation for Pell Grant recipients, while others with one twenty five thousand, or for households two hundred and fifty thousand, and under in income could receive up to ten thousand dollars in cancellation of debts. Another part of this plan is that anyone who is working under non-profits, military, or any government level might also be eligible to get their debts completely canceled through the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program. The third part involves trying to get payments towards debt to not be as steep as needed and reduce how much families would have to pay monthly on their debts. These steps include things such as making caps for how much they have to pay back based on disposable income, reconsider how much is disposable income so that no one under about a fifteen dollar minimum wage for a single borrower isn’t forced to pay back monthly. Another way they are forgiving debt after ten years of borrowing instead of twenty years, as well as the government will cover any unpaid monthly interest. This all together will make it more fiscally possible for many families to repay burdensome loans, as well as allow students coming out of college to start families and possibly start businesses with these new breaks on loans from college. This growth in ability for families and many who have been unable to pay off them before.
For more information go to https://studentaid.gov/debt-relief-announcement/ to see more specific information about the Biden Administration’s plan for student debt.
Your donation will support the student journalists of Willis High School. Your contribution will allow us to purchase equipment and cover our annual website hosting costs.

Michael Scholwinski is a 1st year newspaper staff member who has been active in many aspects of school life. A previous football player and current wrestler,...